July 6th is celebrated as World Zoonoses Day every year to commemorate the scientific achievement of the first vaccination against zoonotic diseases. Zoonotic diseases are infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites that spread between humans and animals.
The first vaccine was administered in humans in the year 1885, on July 6th, by French biologist, microbiologists, and chemist Louis Pasteur developed to fight the Rabies Virus. Though, today the world is suffering from another deadliest zoonotic disease which is novel coronavirus pandemic.
At present, microbiologists, chemists, and researchers are working relentlessly to develop a vaccine to save human civilization from this disease. Hence, this day becomes all the more important for us in 2020 – the year of the Novel Coronavirus pandemic.
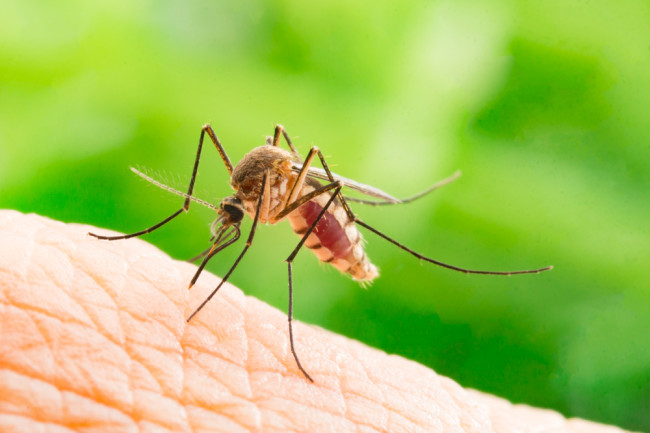

How zoonotic diseases spread?
Zoonotic diseases spread from direct contact between infected animals and humans. These animals can be from infected poultry animals, reptiles, amphibians, rodents, insects, and other domestic and wild animals.
An insect bite is a very common mode of spreading zoonotic diseases, especially through the bite of a mosquito.
The most common zoonotic diseases are: Plague, Tuberculosis, Cat Scratch Fever, Tick Paralysis ,Hantavirus, Ringworm, Salmonellosis, Leptospirosis, Lyme disease, Campylobacter infection, Giardia infection, Cryptosporidium infection,Roundworms, Hookworms, Scabies, Harvest mites, rabies etc.